According to Marketsand Markets, the global post-pandemic log management market is expected to grow from USD 2.3 billion in 2021 to USD 4.1 billion by 2026.

The above analysis from Precedence Research points out the global log management market size is projected to be worth around USD 10.08 billion by 2034 from USD 3.27 billion in 2024.
The enormous volume of data produced by networks and connected devices, as well as the incorporation of technologies such as AI, ML, and predictive analytics into log management to extract insights from the log data, are the main factors propelling the log management market. Let’s review the fundamentals before delving deeper into the usefulness of logs as a source of practical insights.
What is a log?
Log is an audit trail record that captures all the events that occurred in the application or infrastructure with the timestamp. In the real world, all the applications whether small, medium, or large will produce logs. Even the system and infrastructure have their own log files.
Some Types of Logs
- Web Server Logs
- Network Logs
- Application Logs
- Container Logs
- System Logs
- Security Logs
When logs come in handy?
Logs are the go-to files that one needs to check when an issue occurs with the application or infrastructure. Through logs, we can identify the issues and resolve it.
Who uses Log Files?
Log files are used in various ways by different professionals. These are a few instances of the many kinds of professionals and their log file usage.
ITOps Team: Log files are used by ITOps to assess the state of an organization’s IT infrastructure, assisting them in managing workload, minimising downtime, maintaining smooth operations, and lowering operational and financial risk.
DevOps Team: Log files are used by DevOps engineers to monitor CI/CD, maintain the smooth operation of applications, identify problems before they cause downtime, and enhance performance.
IT Analyst: Log files are used by IT analysts to report on capital expenditures (CapEx) and operating expenditures (OpEx) and to control compliance.
What is the difficulty in reading logs?
An application’s log file, which records every occurrence, is quite large and heavy. Depending on its size and complexity, an application can write up to 1000 log lines per second. Also, more than one log can be written by a single application. Reading and analysing thousands of lines of logs to identify a possible problem is not doable for humans. It is a time-consuming procedure that results in SLA violations and financial losses even when several resources are used to analyse various log files.
Rise of internet-connected devices
The internet-connected network devices today generate a large amount of log files. According to a research, various network devices generate 10,000 log entries daily that can be up to 4 GB in size for medium-sized companies. Furthermore, businesses are facing problems in managing and storing the log data.

Expertise required to understand different log format
Data from log files is produced by different systems and can be unstructured, semi-structured, or structured. However, for developers and administrators to use logs accurately, they must be processed or examined line by line. Parsing becomes more difficult and time-consuming when there is no logging standard.
Speed
The amount of time needed for log management may rise due to the volume of logging data and the parsing needs. As ineffective log management systems process logs slowly, they hinder organization’s ability to act quickly.
What are various kinds of tools used in log analysis and management?
Log analysis tools | These tools assist administrators to diagnose problems and enhance system performance by analysing logs to find patterns, anomalies, and trends. |
Log collection tools | These tools gather logs from various IT components, compile them, and keep them in one place. |
Log search tools | These tools assist administrators to search logs according to various parameters, including source, severity, and time. |
Log visualization tools | These tools make log data easier to grasp by presenting it in graphical representations such as dashboards and charts. |
Understanding log analysis and log monitoring
Log analytics helps in assessing and understanding historical log data to detect issues quickly. An alert requires investigation into the logs to understand exactly what happened and the analysis is useful for keeping the health of application from all perspectives including security, business analytics, and compliance.
Log monitoring is a process of observing real-time logs to collect information and trigger alerts based on the findings revealed from log analytics.
Two distinct ideas—log monitoring and log analysis—combine to speed up the process of fixing problems with a system or application. To put it simply, log monitoring is the often-automated process of gathering logs and notifying the organization’s key personnel when a problem is discovered. The next step is log analysis, which frequently entails using a log management system and related tools to efficiently and rapidly identify and fix a problem.
Pandemic-driven digital transformation driving rise in log monitoring and analysis
Pandemic has forced business to adopt digital transformation that has increased the number of access points. As a result, companies are experiencing a rapid increase in event log data demanding log management solutions.
Organizations are now concentrating on centrally controlling various cloud resources as a result of COVID-19. This makes log data even more crucial for assessing and enhancing the security and performance of networks, endpoints, and applications. Additionally, log data can assist you in locating and resolving critical problems that can enhance performance rapidly. Log management services and solutions that gather and correlate log data from cloud services, applications, and infrastructure are therefore in more demand. Log management aids in performance evaluation, configuration optimization, and problem identification.
A significant amount of distributed log data will be produced for every new device as the COVID-19-induced digital transformation boom increases reliance on IT. The analytical method is made much more challenging and time-consuming by the exponential expansion of log data following the occurrence of COVID 19. The log analysis procedure is made more difficult by the absence of a uniform log format. Threat intelligence can be practiced more quickly and effectively by organizations using the standard log format.
The exponential increase in log data post pandemic has made the analysis process even more complicated and time-consuming. Logs help in identifying and resolving critical issues. By using AI and ML in log analysis, millions of log lines can be analyzed to mine distinct patterns that can point to future threats. Many companies are either adopting remote or hybrid work models. Thus, the role of log management for security assessments is even more significant than before for effective security information and event management (SIEM).
How ignio Observe helps?
The most powerful and unique feature of Observe is log mining. This feature differentiates Observe from other monitoring tools available on the market. The user needs to only collect the log files from any application or infrastructure and feed the logs to Observe’s log mining algorithm. Observe then mines millions of log mines within a few minutes and identify distinct patterns. The user gets the mined patterns as the output.
This is a sample of mined patterns.
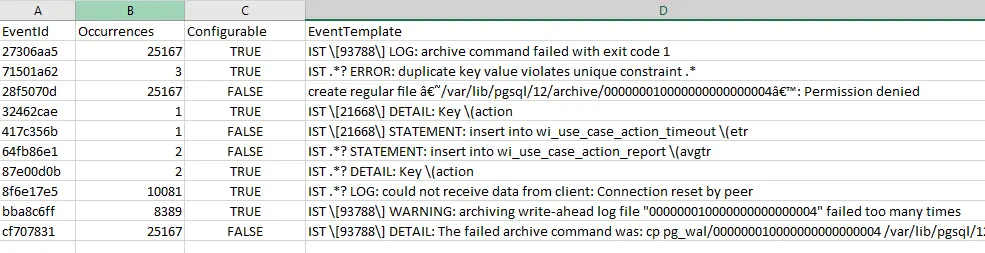
From the output, an IT command center member can easily understand the most recurring pattern and take the action accordingly. Further, with Observe’s log monitoring, a user can select any of these patterns and configure them to be monitored in the real-time log data. ignio Observe is an add-on module of ignio AIOps. With Observe, Digitate has further strengthened and completed its offering in AIOps domain, by developing features of the three pillars of AIOps as defined by Gartner: Observe, Engage, and Act. The raised events are sent to ignio Event Management for noise suppression and self-healing.
For more information on ignio Observe and its features, you can visit our website or contact us here for a detailed demo.
