There is an ever-increasing focus on collecting and analysing data in almost all industry verticals ranging from retail and hospitality to banking and finance. But today’s businesses struggle when it comes to understanding data or data-driven insights. The data is too much to consume, and the data-driven insights are too complex to process. This is creating a rampant gap between the potential of data analytics and its adoption by businesses. Data visualization can act as a very effective vehicle to bridge this gap. Data visualization today is not just limited to generating reports and dashboards, instead, it is becoming a system of engagement for the end-user to get familiar with the data and make use of the data in the best possible way.
Data visualization has come a long way. Its evolution has been driven by the advances in technology, the advances in data, and the advances in the creative ways in which businesses are using data.
- Before the advancement of modern technology, early visualizations of pre-20th century primarily relied on simple visualization representations such as tables, charts, and maps.
- The 20th century then saw more standardized techniques of static charts. The data was represented using tools such as line charts, bar charts, pie charts, scatter plots. These representations allowed users to visualize data in a structured and comprehensible manner.
- Advances in computer graphics in the late 20th century then paved the way to graphical user interfaces. Data visualization entered the space of dynamic and interactive visualization.
- The rise of bigdata, led to greater depth and sophistication in visualizing multi-dimensional and complex data sets through heatmaps, treemaps, network graphs, and 3-D visualizations. Platforms such as D3.js, and tools such as Power BI and Tableau enabled users to interpret massive amounts of data quickly and intuitively.

Going forward, data visualization is headed to revolutionize how we interact with data by creating immersive, interactive, and personalized experiences. Different factors are playing a crucial role in shaping the future of data visualization. In this blog, we discuss three critical aspects that are driving the trends in data visualization.
- Advances in observability and big data — Businesses have an increasing focus on observability. Data is getting collected and analysed across all layers of business, application, and infrastructure. The need to analyse such large, complex, and multi-dimensional data is influencing the future of data visualization.
- Advances in AI — Like most industries, AI has a strong influence in shaping the future of data visualization. New possibilities are opening with low-code and no-code development and automated UI generation. Generative AI is making technology accessible in never-before-seen ways.
- Advances in technology — Technology advances are driving the trends to create animated, interactive, and immersive visualizations.
In this blog, we discuss some of these trends that are shaping the data visualization of today and tomorrow.
Trends Impacted by Advancements in Observability and Big data
Data observability is the process to understand, measure, and track the health of data as it flows through the system to ensure accurate and trustworthy decision making. Data observability drives 3 key trends in data visualization.
360-degree views — With so much data being collected, there is an increasing focus on presenting a comprehensive 360-degree view of the system by connecting the dots across a wide-variety of data sources. Various industries are making use of such views and are coming with more requirements for such bird’s-eye views. Below are some examples:
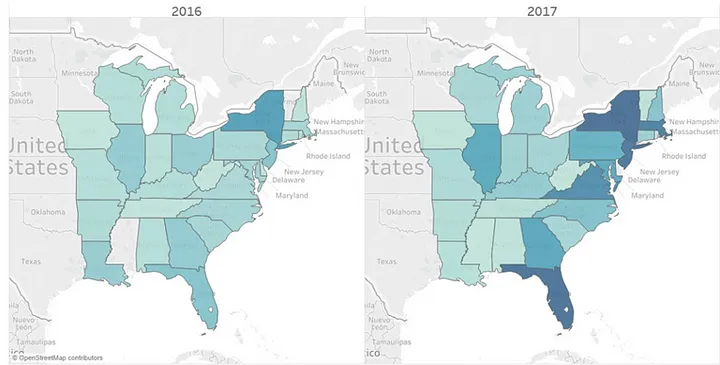
- CFOs of ecommerce websites often make use of such views to quickly glance on the area from where maximum hits come to the website. Below figure shows one such view where the darker areas indicate higher website visits.
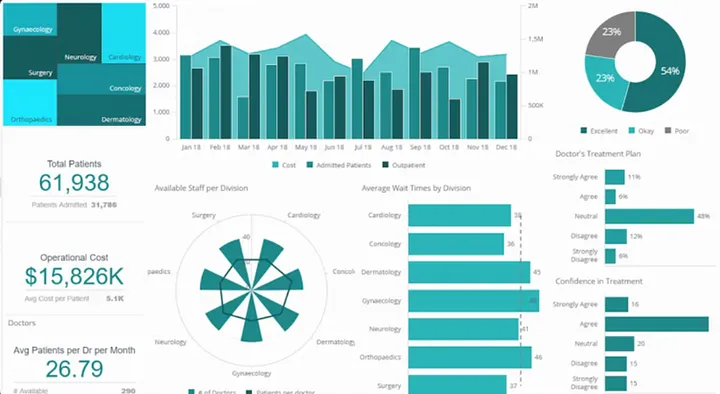
- Hospitals make use of such views to get a clear view of their overall performance and identify the gaps to improve the overall patient experience. Below is an example of one such view.
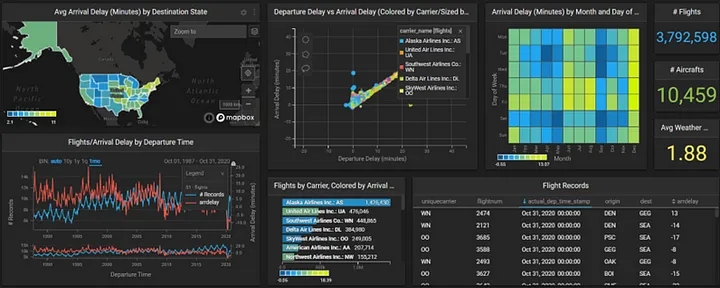
- Aviation industry makes use of such views to understand the performance of an airport in terms of delays and cancellation. Below figure shows one such example.
AI, machine learning and IoT together can enhance the capability of 360-degree visualization making it a crucial element in the world of monitoring and management. One of the major challenges in 360-degree visualization is that the target audience can be different for a single holistic view shown as part of the data representation and grouping the information together on a single pane should reach the right audience.
Real-time visualization — Providing a real-time view of data is another fast-picking visualization trend. It is often used to bring transparency, track inconsistencies, and better understand the current system state. Flight tracking presents an interesting example of such visualization that gives a real time picture of number of flights flying across at a particular point in time.
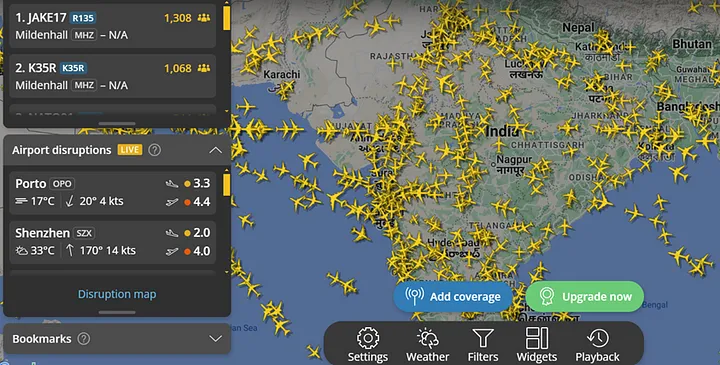
With real time information, the quick data processing and immediate visualizations help users to conclude on any business-critical decisions. Some of the common challenges in real time data visualization is:
- The volume of data coming into the system, this can sometimes be overwhelming for the user to process and understand.
- The response time or the time taken by the data to process and update the results can vary based on the incoming load. For example, in stock market, a delay of just a few milliseconds can mean the difference between a profitable and unprofitable trade.
- If the quality of the data is low and contains erroneous or missing information, can completely change the final visualization which in turn confuse the user on the authenticity and correctness of what is shown on the dashboard.
Intuitive narrow-downs — Once an effective visualization is presented to the end user, based on the user persona who is analysing the charts or graphs there should be handles to highlight the area which needs attention. There is an increasing demand to provide ways to aggregate data, filtering out the unwanted data, concatenate multiple charts/graphs together for faster decision making, and other such tools to make it easy to narrow down the insights of interest.
Trends Impacted by the Advances in AI
AI is empowering the UI designers and developers to focus on core creativity by giving them several tools as disposal. GenAI will play a pivotal role in augmenting data visualization platforms where AI and user can collaborate on the same canvas, empowering users to curate their own experiences.
Automated dashboard creation — AI/ML algorithms are heading towards automating the process of data visualization. These algorithms can generate visualizations that best present the data and data-driven insights. Some tools are already available that help to quickly convert data into dashboards without much manual intervention. One such tool is Ajelix BI that simplifies the dashboard creation in just 4 steps. Below figure presents one such dashboard.

Natural language interactions — Advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural Language Generation (NLG) are paving the way for simpler interaction metaphors where users can interact in natural language queries through voice or text. Instead of staring at elaborate dashboards, data visualization is likely to head towards simpler interfaces allowing users to simply ask for the information of interest.
Customization and personalization — AI is sharpening the ability to analyze user behavior and assess user’s preferences. This can be leveraged in powerful ways to create adaptive visual experiences. AI can adjust the dashboard layout, the content, the visualization metaphors, etc., based on the user’s behavior and preferences.
No-code/low-code tools- AI is offering low-code and no-code solutions to create dashboards. This will make it very easy to create insightful visualizations without the technical skills of data visualization. There are several tools in the market that are now offering such capabilities. With Polymer’s AI capability, data can be quickly transformed into customized dashboards. Other similar tools offering a no-code or low-code way are ‘VisualizeFree’, ‘Qlik sense’, ‘DronaHQ’ etc. An interesting example in this space is “Goodgigs”, a marketplace for freelancers, that is built completely using a no-code app builder.
Trends Impacted by the Advances in Technology
Technology has played a strong driving force behind the evolution of data visualization, and it continues to do so. With powerful computing systems, sophisticated algorithms, and advanced visualization software, data visualization is reimaging the way end users engage with data and data-driven insights.
Mobile-friendly visualization — Today, mobile impressions are often the first impressions. Mobile-friendly and mobile-optimized visualization continue to drive trends in data visualization. There is an increasing need to focus on properties that allow visualization that can be viewed seamlessly across multiple platforms.

Following are some of the common challenges observed in mobile data visualization:
- Limited interactions: Unlike laptop or other large displays, where the interactions can be using mouse or multiple other keyboard keys, it is difficult to show the same visualization in a mobile device in the as-is format. Because of the limited estate, the visualizations should be altered to bring in a view where fewer interactions are needed. Users commonly face issues such as the fat finger problem or the no-hover design, which limits the interactions in mobile device. Consider this example scenario: Emily is a mother of a 10-year-old girl. While coming back from work, she sees her daughter’s annual assessment report on the school’s application. There are large number of parameters in which the student is assessed, and parents must provide an approval or decline if there are any clarifications required. While Emily is still checking the report, due to shaking of the mobile phone in the bus, she accidentally chooses the accept button which send a confirmation to teacher that no clarifications are required which might not be the case.
- Misleading visualizations: There are scenarios where limitations in the screen space have led to designs that compromise with the ease of use of information that is shown to the user. Example scenario: Olivia has been prescribed to take insulins when her sugar level reaches a certain limit. Her blood sugar monitoring device sends data to the health app to track the details. When she checks the health app, she is confronted with a complicated interface which brings up other health information such as blood pressure, exercise details, energy levels, screen time, sleep cycle, steps etc. This creates frustration of not finding the relevant information quickly and easily.
Animated and interactive visualization — Static data visualization is no longer sufficient. The attention span of the users is reducing. Animations provide an effective tool to catch-up with this trend to keep the user engaged. Basic data animations have been present since last few decades, but they offered flashy and imprecise visuals. Latest advancements in animated and interactive visualizations provide effective vehicles to summarize insights without excessive text and to provide interactive drill-downs into the areas of interest.
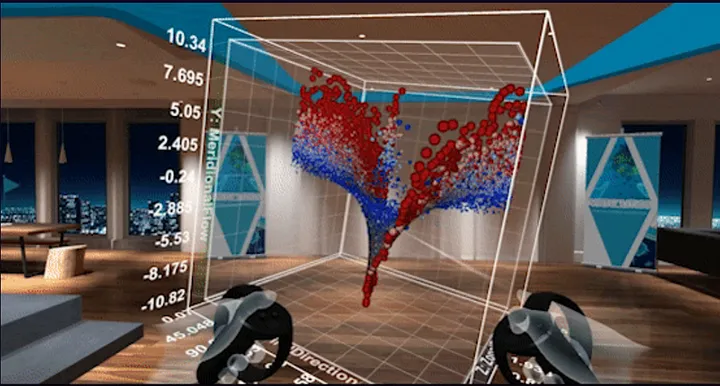
AR/VR immersive experiences — Traditional data visualization technologies restrict the facts and imaginations derived from the data. This problem further accentuates as the data cuts across different layers of technology and business. Many data scientists strongly believe that AR/VR can transform the way users interact with and interpret data-driven insights. AR/VR driven visualizations are still in the initial stages, but it is certainly gaining popularity. Several tools are now enabling creation of creative AR/VR experiences.
- Flow Immersive offers interactive experiences by using AI and 3D visualization to better present and understand data.
- Virtualitics is one of the leaders in the virtual reality space which is helping users with 3D visualization by ingesting big data with hundreds and thousands of metrics.
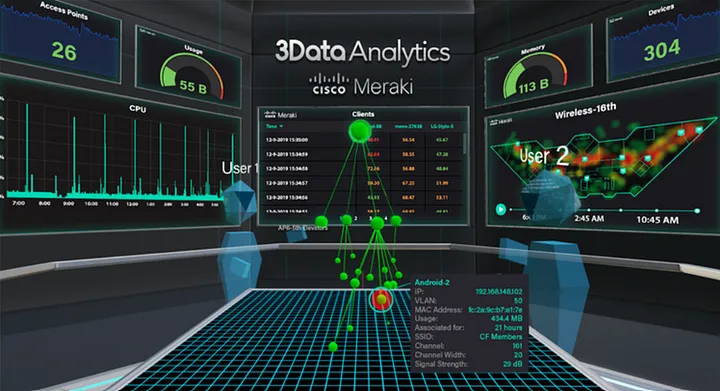
- 3Data focuses on visualizing Enterprise IT, where the devices of an organization can be displayed with hundreds of datapoints. They have a smart assistance called “Apollo” which operates over voice commands.
Conclusion
The future of data and driven-insights is visual. Data continues to grow in volume and complexity, and so does the number of people using it. By embracing emerging trends, data visualization is all set to play a powerful role in data storytelling and driving data-driven decision making.
